Yesterday, June 9, Google announced via Twitter the end of the implementation of the May 2022 Core Update. Let us remember that it was launched on May 25, so its development has lasted 15 days.

Based on data from Google’s algorithm volatility tracking tools, this May 2022 Core Update was a great update that was rolled out quickly for many queries tracked by data providers. After the initial launch, we could see some “shakiness”, some changes in volatility, although the most important peak occurred around 06/05.
Let’s see the evolution of the main monitoring tools:

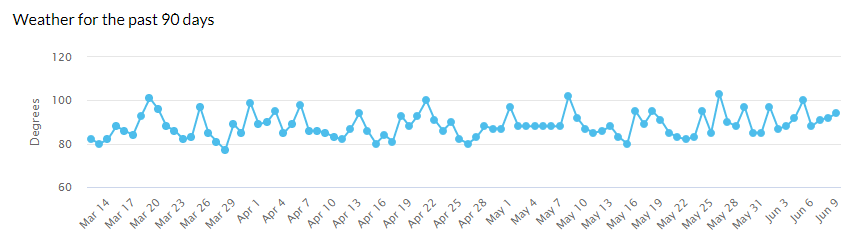

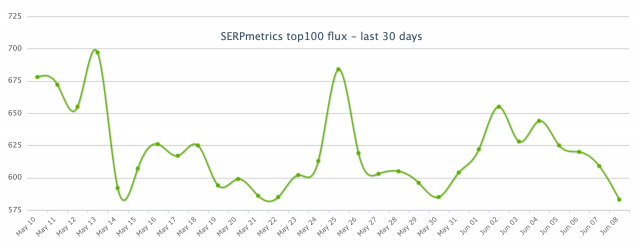
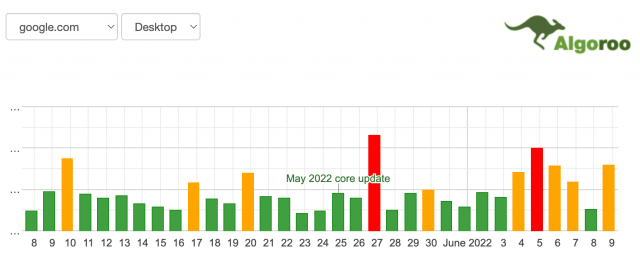
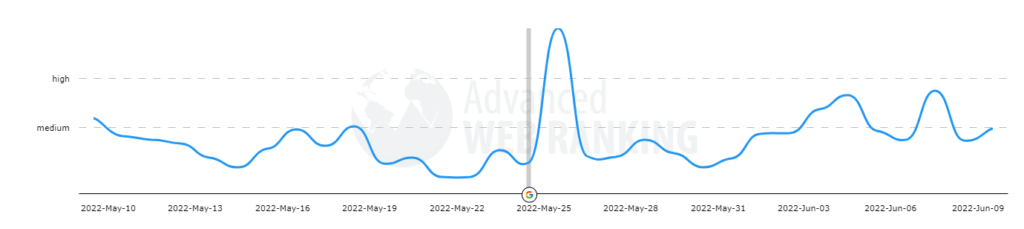

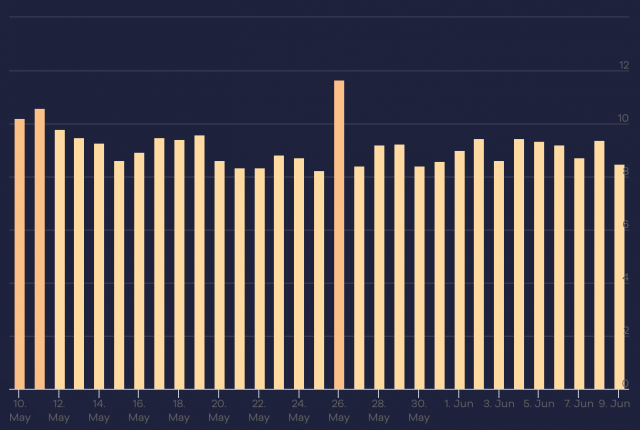
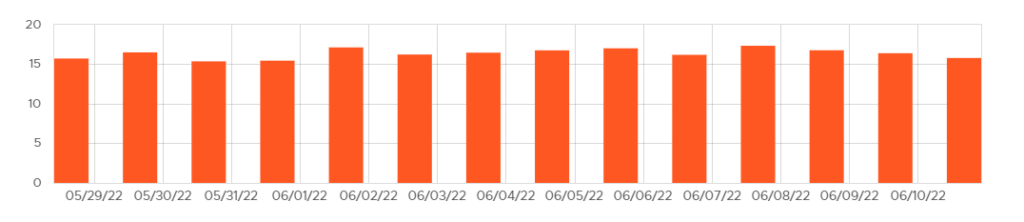
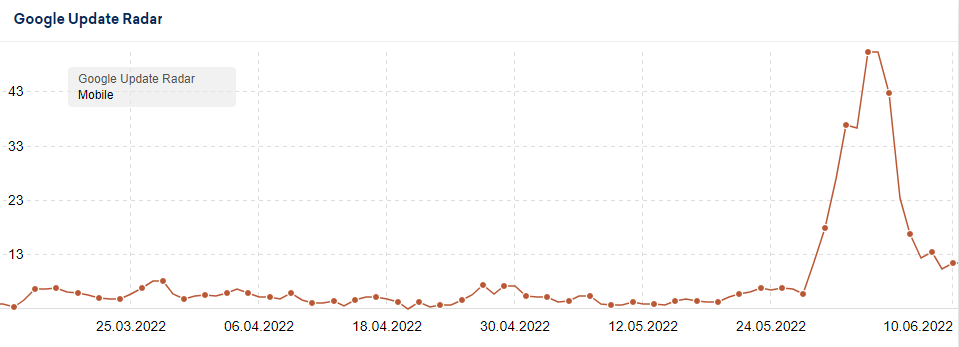
Fluctuations prior to the May 2022 Core Update
Before discussing the impact of this update, let’s talk a little about the fluctuations that we were able to observe a few days before. As we know, the May 2022 Core Update went live on May 25, but a few weeks earlier we were able to observe significant fluctuations that seemed to herald and/or be related to this algorithm core update. Seen with perspective, perhaps that clear relationship does not exist and we can attribute it to another reason. In this case, to the integration as a fixed module of the PAA module (Other questions from users).
The Google search results page is not made up of organic results + modules but rather 10 “result slots” + modules, with a few exceptions. The modules are “an extra” that are added to those spaces, but for Google they do not count as search results as such. Hence, we can position in a module and in organic with the same URL. That is, they are independent.
These modules can change their “state” and occupy one of those. This change is very important, as it happened with the Featured Snippet module (misnamed Position 0) on January 22, 2021. Before, you could position with the same URL in the FS module and in the 1st organic position. But when he was integrated he stole a position from the organic and you couldn’t have that double result anymore.
And that is what has happened now with the integration of the PAAs.
Impact of the May 2022 Core Update
Doing a general analysis of the effects of this update of the core of the Google algorithm, we can see:
- In the first place, a significant rise in positioning among authority websites has been observed. That seems to indicate in aspects related to authority and relevance.
- We could also observe that, in navigational searches, URLs improve reputations (social profiles, for example). This seems to indicate aspects related to entities and reputation beyond digital assets that a brand can control.
- The presence of video and image blocks in the SERPs also increases.
- The drop in affiliate and niche sector sites stands out.
- Positioned URLs are refined when they were not the most relevant to the search intent.
- And branded keywords gain traction on official sites and popular sites.
How the update has affected our accounts
With regard to the accounts that we manage at We’re Sinapsis, 40% have maintained stability, not being affected by this update of the central core of the Google search algorithm. 36.7% have shown an upward trend in their positioning, quite important in many cases. And the remaining 23.3% has suffered a drop in visibility.
From the SEO department of We’re Sinapsis, we are already studying strategies to counteract these falls and we remain attentive to the volatility of the algorithm.
Fuentes: Sistrix, MJ Cachón, Search Engine Land

